Why ADHD is linked with Addiction
ADHD and Substance Abuse
Recently, a paper[1] came out stating that half of the adults with ADHD experience or have experienced a substance use disorder. Alcohol use disorder is most common among adults aged 20-39, followed by cannabis use disorder and other drug use disorders. In addition, more than one-quarter of those with ADHD experience major depression.
To understand ADHD better, it's important to know that it's a disease of executive dysfunction. Our executive function is our brain's capacity to plan and execute tasks, inhibiting certain behaviors and impulses in order to do the task.
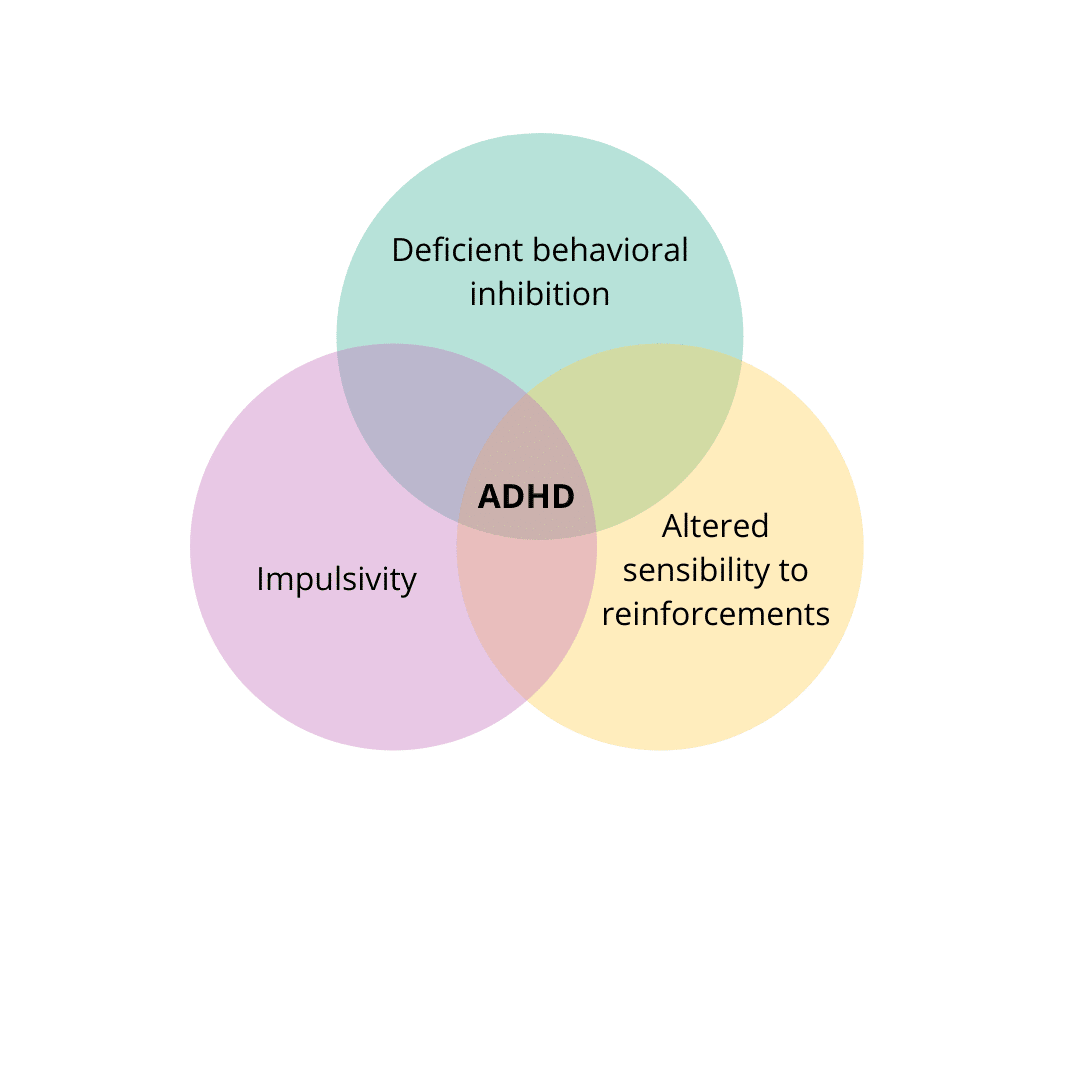
The first thing is that people with ADHD have a deficiency in their behavioral inhibition circuitry. Secondly, they have altered sensibilities to reinforcements, which means that things that are low-hanging fruit and easily enjoyable are far more enjoyable to people with ADHD. They'll prefer more instant gratification. Thirdly, people with ADHD are more impulsive, meaning that when they have an impulse, they're much more likely to act on it, correlating to the other aspects of ADHD. The impulsivity also relates to intolerance to delayed gratification.
The ADHD brain is very vulnerable to substance use because of these three things.
ADHD Neuroscience
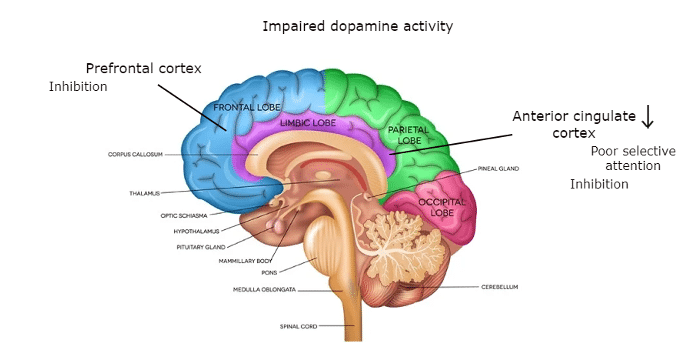
There are different areas in the brain related to ADHD.
One of the most affected ones is a part in the front of your brain called the Prefrontal cortex, which is responsible for inhibition.
Another part is in the center of your brain, called the Anterior cingulate cortex. Its dysfunction results in poor selective attention and low inhibitory control. People with ADHD have reduced activity there.
People with ADHD also have impaired dopamine activity across the brain.
Essentially, what happens in the ADHD brain is getting too many thoughts too fast; the brain is not able to turn down the volume of some thoughts.
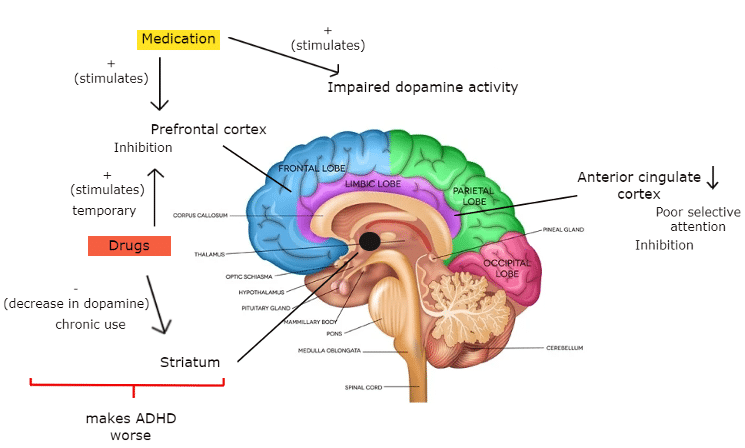
By giving people with ADHD stimulant medication, you're stimulating an area in the front of their brain (Prefrontal cortex), increasing inhibition and allowing them to focus on one thing. The medication will also increase dopamine levels.
Baseline low dopamine generates ADHD symptoms, and taking drugs will increase the dopamine activity, resulting in almost self-medication. The problem is that this effect is temporary, and it leads to other impacts, like the stimulation of the hippocampus. Over time, it'll affect the part of our brain called the striatum, decreasing dopamine and making ADHD worse.
Mechanisms of ADHD
ADHD and substance abuse reasons
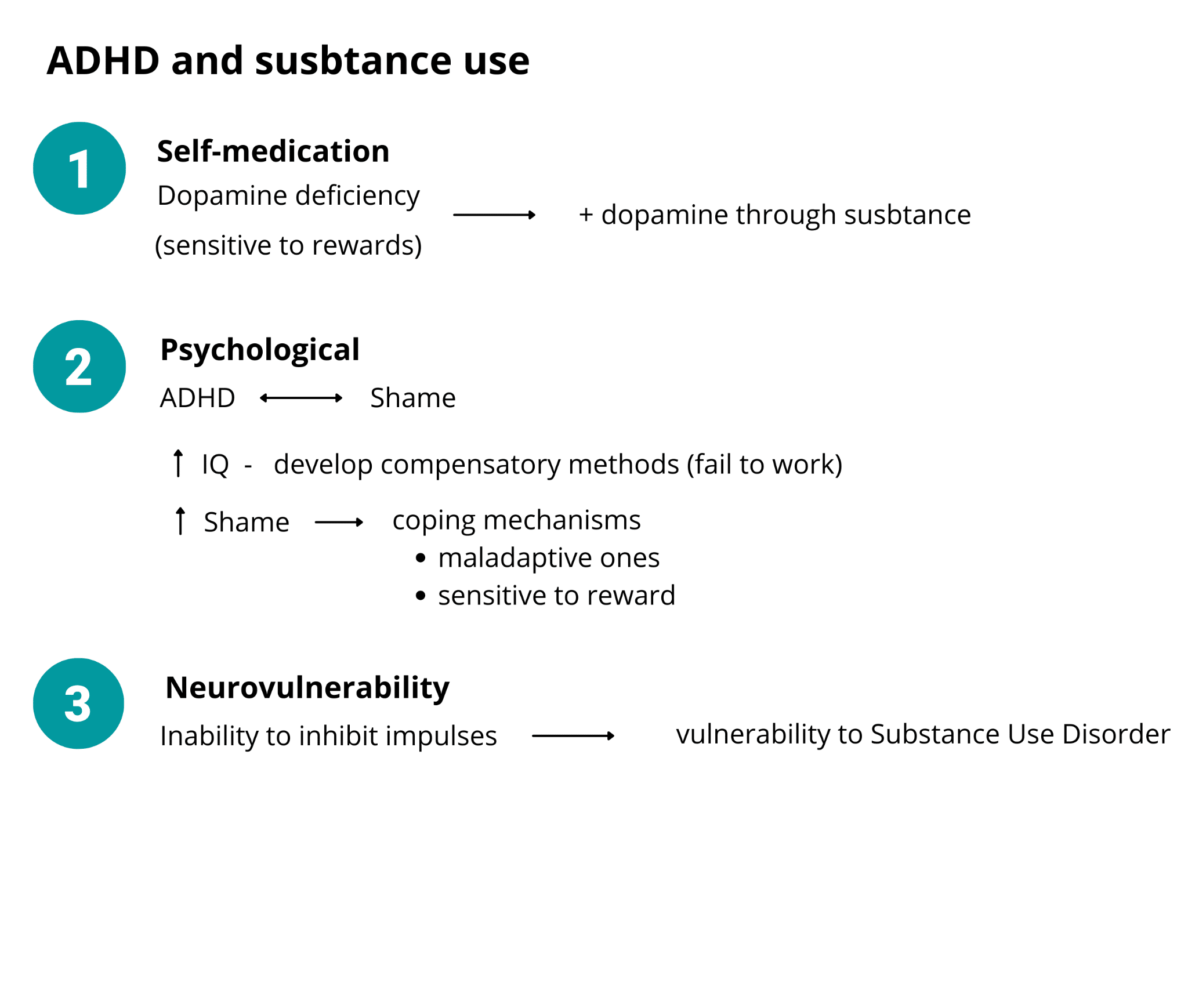
The first reason why people with ADHD use substances is to self-medicate.
The ADHD brain is dopamine deficient, which is part of the reason why they're sensitive to rewards.
Drugs will increase dopamine in the brain for a while, and that's also why ADHD medicine is a stimulant.
The second reason is psychological.
ADHD is associated with shame; many times, people with ADHD don't understand they have it, and they just feel like they're busted in some way.
Often, those people have high IQs, and they end up developing compensatory methods that require a lot of effort to "keep up" with others. Over time, these compensatory methods no longer work, resulting in more shame. The more shame you have, the more you need coping mechanisms. Then, because the brain is sensitive to rewards, the coping mechanisms end up being maladaptive, such as drugs, video games, or social media.
The third reason is neurovulnerability.
The alterations in the ADHD brain lead to an inability to inhibit impulses, leading to vulnerability to substance use disorders.
What do we do about it?

The first thing is to stop separating ADHD from substance abuse. Suppose you have a motivational problem or ADHD and use any kind of stimulating substance. In that case, this cycle will keep going in your brain, making it hard to be motivated. The substance will contribute to the problem, making it essential to get sober.
You have to deal with the shame linked to ADHD. That's why psychotherapy is a good idea. It's necessary to deal with the feelings that make you reach for that substance.
Do a dopamine detox. Substance use is literally making ADHD worse. You have to give yourself a chance to reset whatever your natural dopamine circuitry is, so you can start responding in healthier ways.
You have to meditate. All of the solutions are basically removing bad things. The one thing you can do to add is meditating. Meditation strengthens your frontal lobe, strengthening the control of impulsivity.
Recognize that you're prone to certain weaknesses based on your environment, so it's crucial to control it. For example, social media and video games are gonna pull the person with ADHD's brain much more than a neurotypical person. Because of the lack of impulse control and the sensibility to reward, it's like you're walking a tightrope, and any gust of wind can blow you off course. That's why it's essential to control your environment.